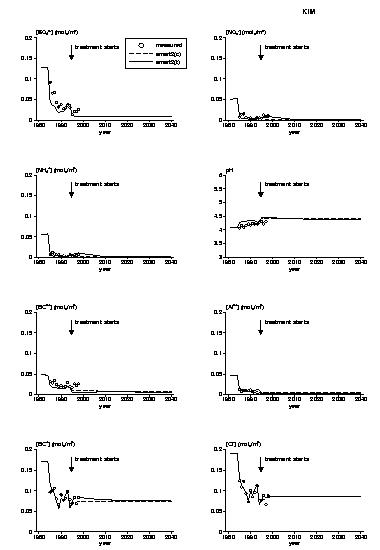
In order to get insight into effects of climate change, temperature dependency of mineralisation, gibbsite constant and weathering was included in the SMART2 model. To test this extension, SMART2 was applied to two manipulated catchments at Risdalsheia, Norway. SMART2 was calibrated at the EGIL catchment, which receives ambient deposition and soil warming from 1994 (Figure 1). Afterwards the model, with the same parameter set, was applied to the KIM catchment, which receives deacidified deposition from 1983 and air warming and CO2 increase from 1994.
SMART2 predicted the effect of deposition reduction very well (Figure 2). The observed increase in N leaching was simulated well by SMART2 especially at the KIM-catchment. To predict long-term effects of climate change the existing treatments of both catchments were extrapolated for 50 years. SMART2 predicted a temporal increase in N-leaching due to temperature rise. In the long term SMART2 predicted decreasing aluminium concentrations and pH as a result of a decreased gibbsite constant due to temperature rise. To validate SMART2 in its performance simulating climate change effects, more data are needed.
Figure 1
Measured and simulated concentrations of SO4, NO3, NH4, pH, BC2+, Al, BC+ and Cl for EGIL catchment.
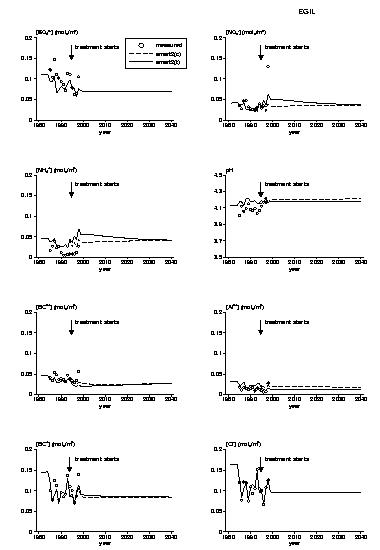
Figure 2
Measured and simulated concentrations of SO4, NO3, NH4, pH, BC2+, Al, BC+ and Cl for KIM catchment.